The creation of new products typically leads to increased resource consumption, energy use, and waste generation, which seems to conflict with the principles of preserving our environment. However, this apparent contradiction is precisely why it's crucial for designers to deeply integrate sustainability into their practice. This integration goes beyond just how things are made; it also critically examines why and what products are made, underlining the importance of creating products that not only last long but also maintain their relevance and appeal over time.
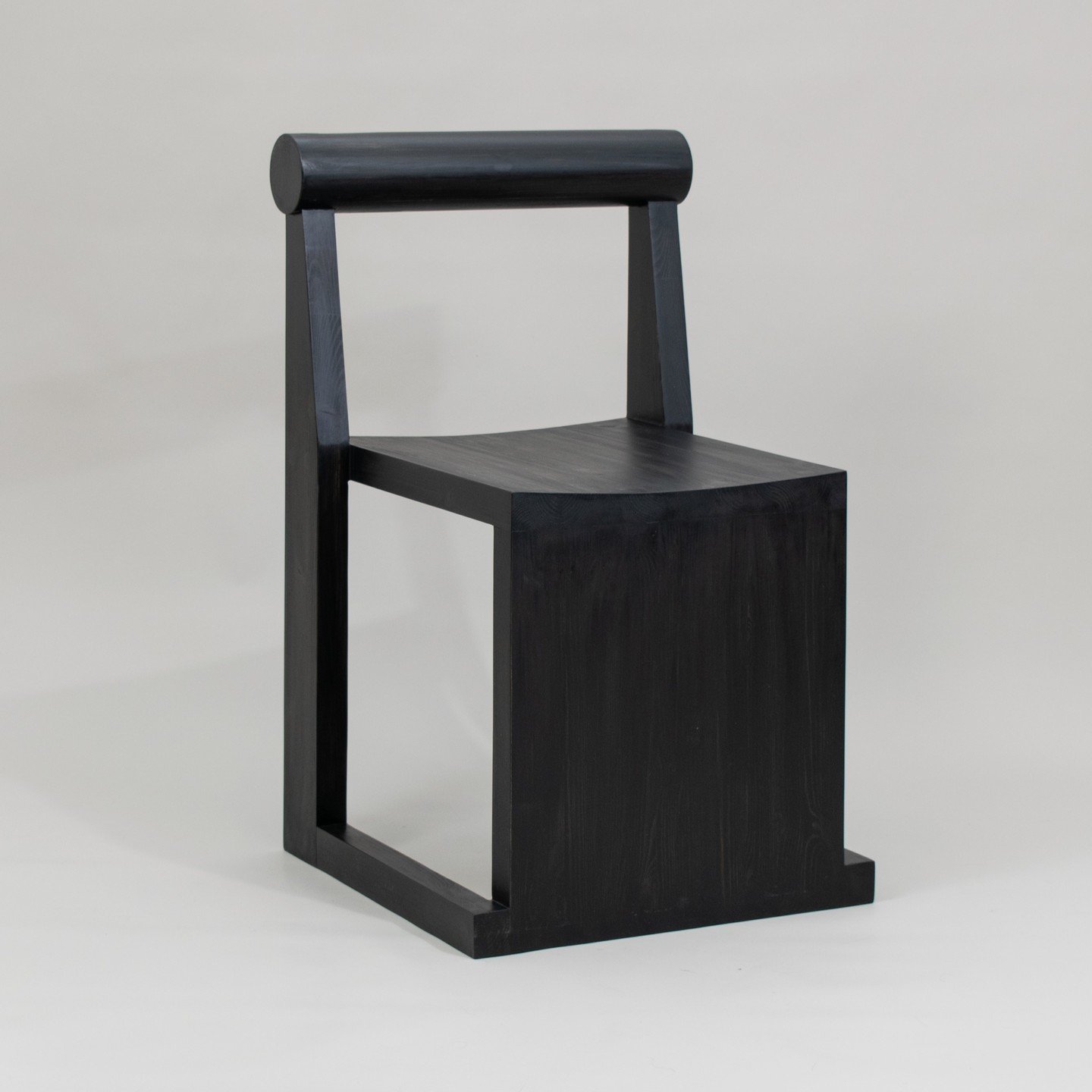
Longevity in products is a key factor in sustainable design. To ensure that products last longer, designers must focus on creating an emotional connection between the product and the user. When people feel a personal attachment to an item, they are more likely to use it for a longer period, reducing the need for frequent replacements and, consequently, lessening the environmental impact.
One effective way to foster this emotional connection is through design that meets the evolving needs of the user. This adaptability ensures that a product remains functional and relevant in the user's life, even as their circumstances or preferences change. For instance, modular designs that can be easily upgraded or reconfigured can adapt to different stages of a user's life, enhancing the product's longevity.
Durability is another critical aspect. Products must be built to withstand the test of time, both in terms of physical resilience and design. This requires high-quality materials and construction techniques, ensuring that the product can endure regular use without significant wear and tear.
However, durability alone is not enough. For a product to remain appealing for decades, it must also be well-designed and visually pleasing. Timeless aesthetics play a significant role in this regard. By avoiding overly trendy designs and focusing on classic, enduring styles, designers can create products that continue to be attractive and relevant long into the future.
In addition to these strategies, sustainable design also encompasses broader considerations, such as how and from what materials products are made, and critically examining the necessity for new products. The adoption of sustainable materials, energy-efficient manufacturing processes, and principles of the circular economy are all integral to this approach.
To accomplish these goals, collaboration across various fields is essential. Designers can greatly benefit from partnering not only with environmental experts, material scientists, and psychologists to better understand and implement strategies for long-lasting design, but also with manufacturers and manufacturing experts. Understanding the nuances of manufacturing methods and working closely with those who are directly involved in the production process is crucial. This collaboration can lead to innovations in sustainable manufacturing practices, optimizing the use of resources, and minimizing waste.
Such partnerships can also provide designers with insights into practical constraints and opportunities in product manufacturing, allowing them to design products that are not only environmentally sustainable but also economically viable and manufacturable at scale.
In sum, while designing new products in the industrial sector may initially seem at odds with environmental sustainability, it is this very challenge that underscores the importance of incorporating sustainable practices in design. By creating products that last longer, resonate with users, and are produced through sustainable manufacturing methods, designers can significantly reduce environmental impact and lead the way in sustainable innovation. This approach not only supports environmental stewardship but also redefines the essence of responsible design in the modern world.
-Simo